
Here’s what I noticed when researching hosting options for small sites in the US: more and more people are talking about cloud hosting today. A few years ago, most beginners only heard about shared plans. Now, every web host seems to promote cloud hosting as the future.
Why? Because websites are changing.
- Traffic can spike overnight
- Online businesses need flexibility
- And users expect fast, reliable sites
This guide will help you:
- Understand what a cloud host really is
- Learn how cloud hosting work behind the scenes
- See how it compares with shared hosting, vps hosting, and dedicated hosting
- And decide if you should use cloud hosting for your site in the US
Let’s keep it simple. From my research, most people just want hosting that works without headaches. No buzzwords. No tech overload.
What Is Cloud Hosting? (Simple Definition)
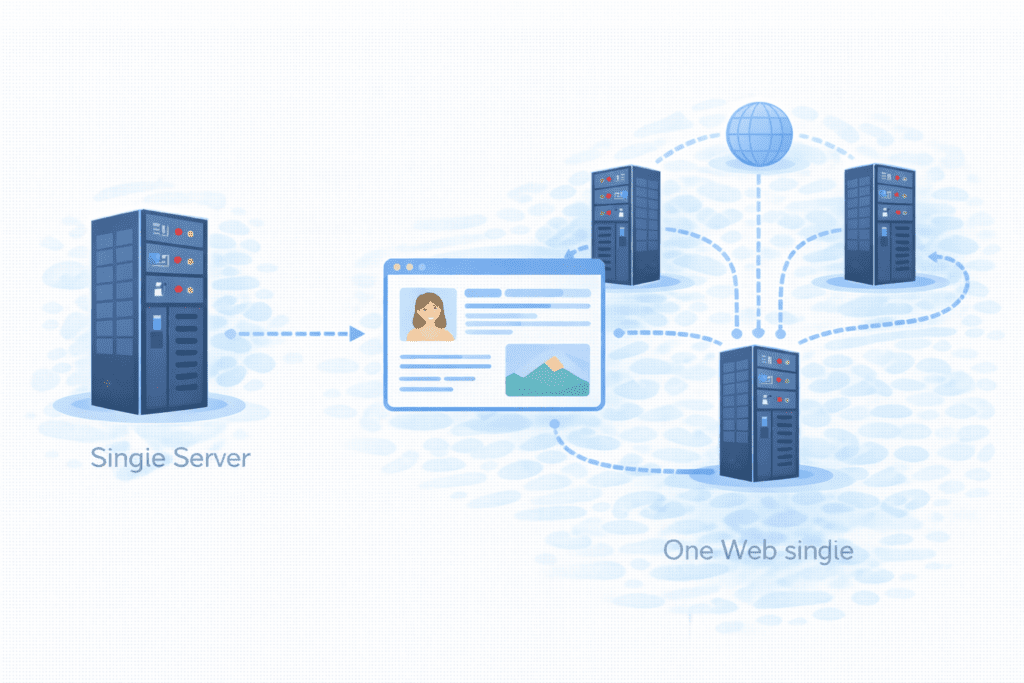
In plain English, cloud hosting is a type of hosting where your website runs on a network of servers instead of one single machine.
A cloud host doesn’t rely on just one physical server. Instead, your site uses many connected servers that act like one big system. These servers live in a cloud environment.
So the simple definition is:
Cloud hosting is a web hosting model where your site uses multiple servers in the cloud to stay fast and online.
This is different from traditional web hosting, where your site usually sits on one physical server.
With a cloud hosting service, if one server has an issue, another can step in. That’s a big reason people like it.
You’ll often hear this linked to cloud computing, which is all about using shared systems on the internet to get flexible power when you need it.
How Cloud Hosting Works
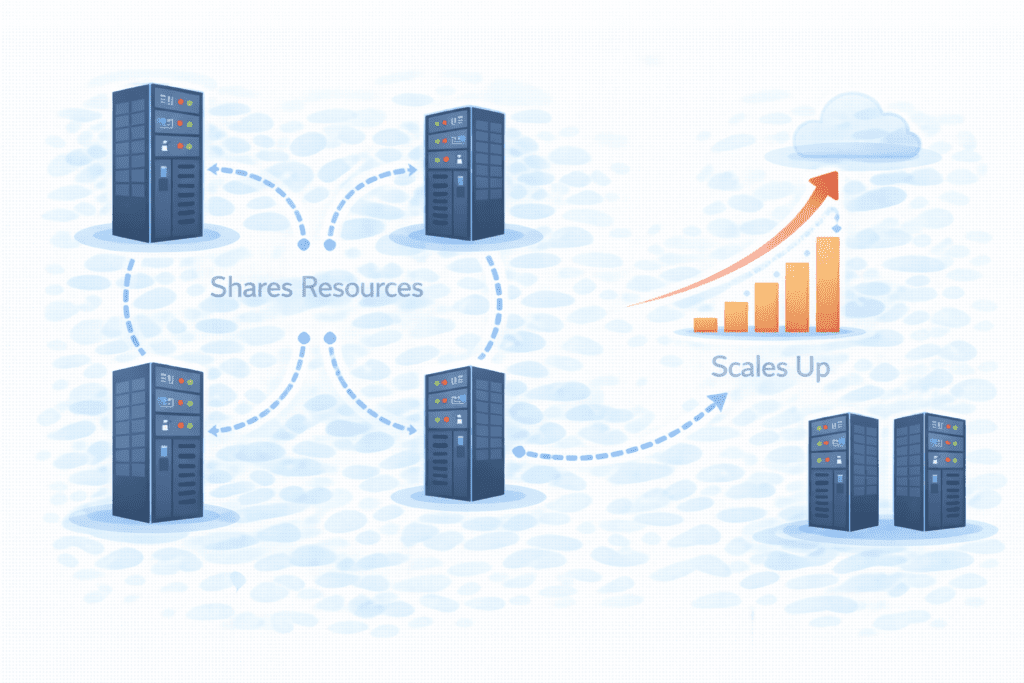
Now this is where beginners usually get confused. Let’s break it down.
A Network of Servers
With cloud hosting, your site runs on:
- Many servers connected together
- Not just one box in a data center
These servers form a cloud infrastructure. Your site can move between them as needed.
Each part of this system can act like a virtual server, even though it’s backed by real machines.
In other words, your website lives on a server in the cloud, not tied to one single computer.
How Resources Are Shared and Scaled
Here’s the big idea:
Cloud hosting gives you access to shared computing resources.
That includes:
- Storage
- RAM
- CPU
- Network speed
If your site suddenly gets more visitors, the cloud host can allocate more computing power. When traffic drops, it scales back.
This is what people mean by scalability. The system is scalable because it grows with your needs.
That’s why cloud hosting uses virtualization — software that turns big systems into flexible pieces you can use as needed.
From what I’ve seen, this is the main reason growing US sites move to the cloud.
What Makes Cloud Hosting Different From Other Hosting Types
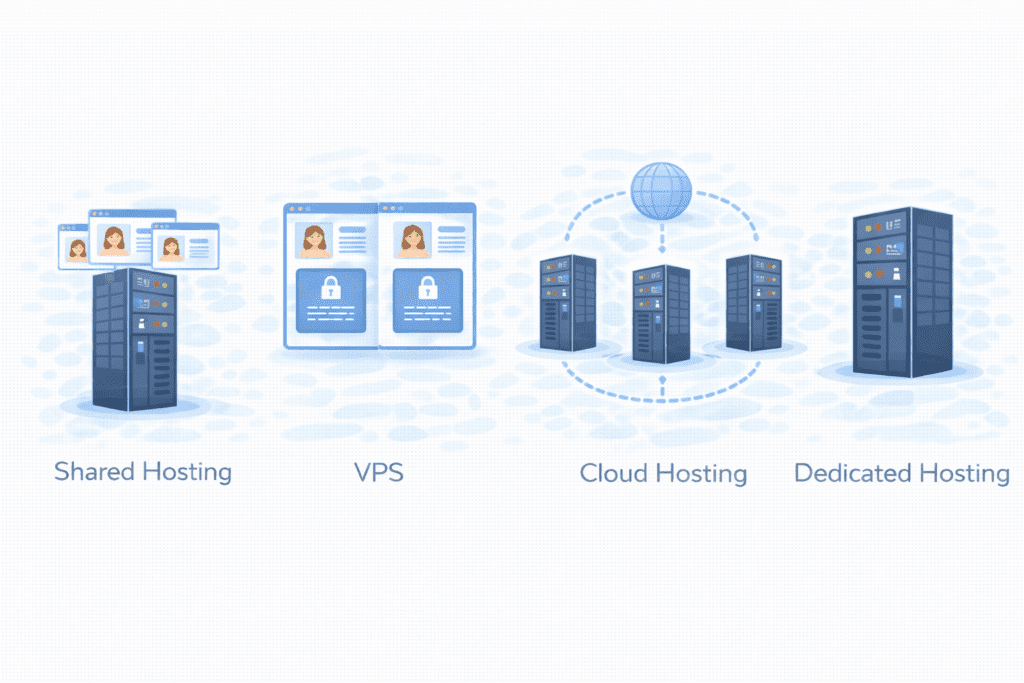
There are many hosting models out there. Let’s see how cloud hosting compares.
Cloud vs Shared Hosting
With shared hosting, your site sits on one server with many other sites. You all share the same resources.
With a cloud host, your site can pull power from many servers.
So:
- Shared hosting = one server, many sites
- Cloud hosting = many servers, one flexible site
This is why people switch when shared plans start to feel slow.
Sometimes beginners ask if they should use shared hosting instead of cloud. For very small sites, shared can still be fine.
Cloud vs VPS Hosting
VPS hosting gives you a virtual space on one server. It’s more powerful than shared hosting, but still tied to one main machine.
Cloud hosting:
- Uses many servers
- Isn’t stuck to one system
- Handles failures better
You might hear about vps cloud hosting, which blends both ideas, but true cloud hosting spreads your site across a bigger network.
Cloud vs Dedicated Hosting
With dedicated hosting, you rent one full physical server just for you.
That gives strong performance, but:
- It’s expensive
- It doesn’t scale easily
- If it fails, your site goes down
Cloud hosting spreads risk across multiple servers. That’s why people compare dedicated or cloud hosting when uptime matters.
Dedicated gives raw power. Cloud gives flexibility.
What Do You Get With Cloud Hosting?
So what does a typical cloud hosting plan give you?
Scalable Resources
This is the big one. A good cloud host lets you:
- Add power when traffic grows
- Reduce it when things are quiet
That’s part of why cloud hosting offers flexibility that traditional plans don’t.
High Availability
Because your site runs on many systems, cloud hosting reduces downtime. If one cloud server fails, another takes over.
This is why many people say cloud hosting is more reliable than traditional hosting.
Flexible Performance
You’re not locked into one machine. The cloud provider can move your site around to keep things smooth.
In most cases, this means better speed for US visitors.
Honestly, from my research, this is what most people really care about: their site stays up and fast.
Who Should Use Cloud Hosting in the US?

Cloud hosting isn’t just for big tech companies anymore. It makes sense for:
Growing Websites
If your traffic is increasing and shared plans feel tight, a cloud host gives you room to grow.
Online Businesses
For any serious online business, reliability matters. Cloud hosting helps keep your site live during busy times.
Traffic Spikes and Seasonal Sites
If your site gets sudden surges (sales, events, holidays), cloud hosting can handle those jumps better.
Many US businesses choose cloud hosting because it adjusts to real-world demand.
Who Should NOT Use Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is powerful, but it’s not for everyone.
Very Small Sites
If you’re running a tiny personal blog with just a few visitors a day, a cloud host might be more than you need. Simple shared hosting is often enough.
Simple Personal Blogs
For hobby sites or test projects, paying for a full cloud hosting solution may not feel worth it. From what I’ve seen, many beginners overthink this part.
Beginners on Tight Budgets
Cloud pricing can change based on use. If your budget is tight and you want predictable bills, cloud hosting may feel stressful.
In these cases, starting with a basic hosting plan from a normal web host is usually smarter.
Key Benefits of Cloud Hosting

Let’s look at the real benefits of cloud hosting that make it so popular in the US.
Scalability
This is the biggest one. A cloud host lets you scale up or down as traffic changes. You don’t have to guess your future needs.
Reliability
Because your site runs on many servers in a cloud infrastructure, it stays online even if one system fails. That’s hard to beat compared to traditional web hosting.
Pay-for-What-You-Use Models
Many cloud hosting providers offer pricing where you only pay for what you use. For growing sites, this can feel fair.
Speed for US Visitors
With data centers across the country, cloud hosting can serve US users faster. The cloud environment helps route traffic to the closest place.
From my research, this mix of speed and flexibility is why cloud hosting keeps gaining fans.
Downsides of Cloud Hosting
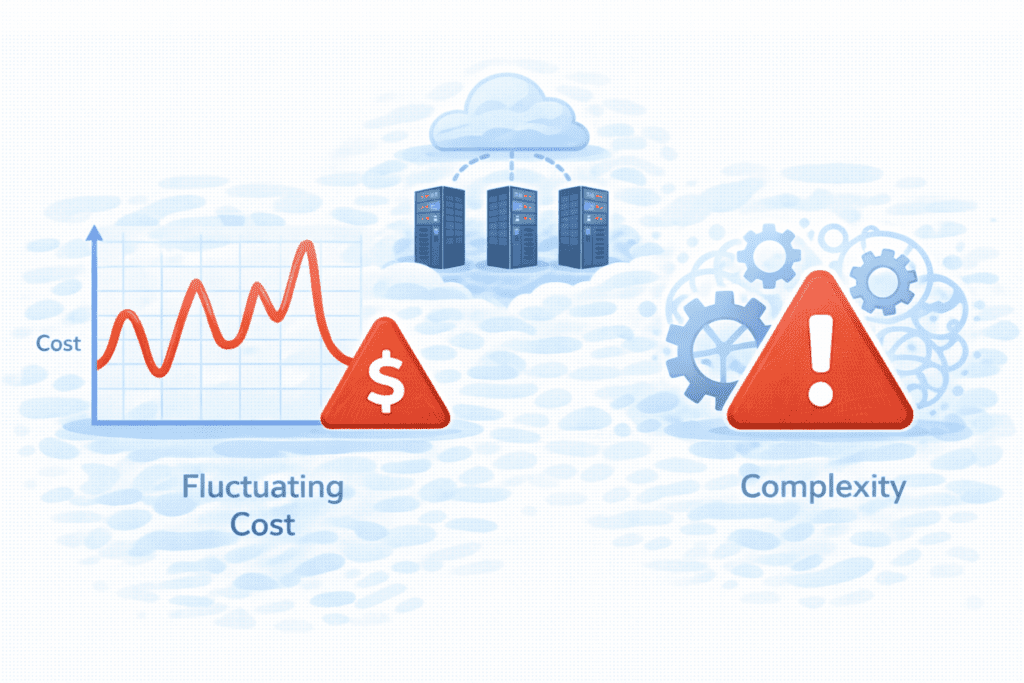
Now, let’s be real about the downsides.
Cost Unpredictability
Because pricing depends on use, your bill can change. For beginners, this can feel confusing.
More Complex Than Shared Hosting
Cloud dashboards and tools can be harder than a simple shared plan. There’s a bit of a learning curve.
Learning Curve for Beginners
If you’re new, concepts like scaling, usage, and settings may feel overwhelming at first.
This is why some people still choose shared hosting instead when starting out.
How Much Does Cloud Hosting Cost in the US?
Let’s talk numbers.
In the US, a basic cloud hosting plan often starts around:
- $10–$20 per month for small sites
- $30–$100+ per month for growing sites
- Much more for heavy use
What affects price?
- Storage used
- Traffic
- Extra features
- Level of management
Some cloud providers like aws or google cloud charge by the hour or usage. Others bundle resources into fixed plans.
So cloud hosting can be affordable at first, but it grows as your site grows.
Is Cloud Hosting Secure?
Yes — when done right, it’s very secure.
Most cloud hosting service providers include:
- Firewalls
- Monitoring
- Regular updates
- Data redundancy
Because data lives across systems, losing one machine doesn’t mean losing your site.
With managed cloud hosting, security is often handled for you. That’s a big plus for beginners.
Still, you’re responsible for:
- Strong passwords
- Updating apps
- Keeping your site clean
Security is shared between you and the hosting provider.
Do You Need Technical Skills for Cloud Hosting?
It depends on the type you choose.
Managed vs Unmanaged Cloud Hosting
With managed cloud hosting:
- The host sets things up
- Handles updates
- Helps with issues
With unmanaged plans:
- You manage servers yourself
- You handle software and configs
For beginners, managed cloud is usually the only realistic option.
Skill Level Needed
You don’t need to be an expert, but:
- Basic hosting knowledge helps
- You should understand your hosting plan
- And know how to read usage stats
In most cases, managed plans make cloud hosting much easier.
Cloud Hosting vs Other Hosting Options
Let’s quickly compare cloud hosting with the main alternatives so you can see where a cloud host really fits.
Cloud Hosting vs Shared Hosting
With shared hosting, many sites live on one physical server. It’s simple and cheap, but resources are limited.
With cloud hosting:
- Your site can use many systems
- Resources grow when needed
- Downtime is lower
That’s why people move to a cloud hosting solution when shared plans feel tight.
Cloud Hosting vs VPS Hosting
VPS hosting gives you a virtual server on one machine. It’s stronger than shared hosting, but still tied to one box.
Cloud hosting spreads your site across a network of cloud server systems, so it’s more flexible than VPS.
Some people compare vps cloud hosting with regular VPS, but true cloud hosting is more dynamic.
Cloud Hosting vs Dedicated Hosting
With dedicated hosting, you rent one full physical server.
Dedicated gives raw power, but cloud hosting offers:
- Easier scaling
- Better failure handling
- Often lower starting cost
That’s why many choose cloud instead of a single dedicated web hosting setup.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make With Cloud Hosting
Here are mistakes I often see beginners make.
Choosing It Too Early
Some people jump into cloud hosting before they really need it. If your site is tiny, shared hosting may still be enough.
Not Monitoring Usage
Because cloud pricing is based on use, not watching stats can lead to surprise bills.
Ignoring Management Needs
Even with managed cloud hosting, you still need to:
- Update your site
- Watch security
- Understand your hosting plan
Cloud hosting is powerful, but it still needs attention.
Is Cloud Hosting Good for Beginners?
Honestly?
Sometimes. It depends.
Cloud hosting can make sense if:
- Your site is already growing
- You expect traffic spikes
- You choose a managed cloud plan
- You want a flexible hosting solution
But if you’re just starting:
- Shared hosting is cheaper
- It’s easier to manage
- And often enough at first
So for most beginners, start simple. Move to cloud when you feel the limits.
FAQs About Cloud Hosting
What is cloud hosting used for?
Cloud hosting is used for websites that need flexibility, steady performance, and easy scaling.
Is cloud hosting better than shared?
For growth and reliability, yes. For cost and simplicity, shared hosting is often better for beginners.
Can I scale down later?
Yes. Most cloud plans let you reduce resources when traffic drops.
How fast is cloud hosting?
It’s usually very fast, especially for US visitors, because data can be served from nearby systems in the cloud environment.
What is cloud hosting and how does a web host deliver it?
Cloud hosting is a hosting solution where websites and applications run on a network of virtualized servers rather than a single physical machine. A web host that provides cloud hosting uses cloud technologies and public cloud infrastructure, private cloud or hybrid cloud configurations to allocate resources like CPU, RAM and storage dynamically. Compared to traditional web hosting models, cloud hosting provides better scalability, redundancy and on-demand provisioning through cloud service APIs and platforms such as amazon web services or google cloud platform.
What are the types of cloud hosting and cloud hosting models available?
Types of cloud hosting commonly include public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud models. Public cloud services are offered by public cloud providers and deliver multi-tenant cloud server hosting on public cloud infrastructure. Private cloud provides a dedicated hosting environment for one customer, often used for compliance or sensitive workloads. Hybrid cloud combines both, enabling burst capacity to a public cloud for peak demand. Other variations include managed hosting and multi-cloud setups across different cloud providers like amazon web services and google cloud platform.
How do I choose a cloud hosting provider and what should a hosting provider also offer?
When choosing a cloud hosting provider consider performance (CPU, RAM, SSD), network bandwidth, SLAs, security controls, backup options and support. A good hosting provider also offers clear pricing models, managed services, and integration with cloud technologies such as amazon elastic compute cloud or Google Cloud services. For many businesses selecting the right cloud hosting means balancing cost, compliance and scalability while verifying that the hosting provider provides a reliable cloud hosting environment and public cloud services as needed.
What is the difference between cloud hosting vs traditional server hosting or a type of web hosting?
Cloud hosting uses a distributed pool of resources across multiple virtual servers, while traditional server hosting typically assigns a single physical server to a site (shared, VPS or dedicated). A type of web hosting like shared hosting has fixed resource limits and is less resilient to spikes, whereas cloud server hosting can scale resources on demand and provide higher availability. Cloud computing environment designs reduce single points of failure common in traditional web hosting models.
Can cloud hosting be used for my web server and what cloud service options exist?
Yes, cloud hosting is well suited for web servers and comes with multiple cloud service options: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) for raw compute and storage, Platform as a Service (PaaS) for managed runtimes, and managed hosting for full maintenance. Public cloud providers offer public cloud services and tools to deploy web hosting that uses cloud technology, while private clouds support organizations needing dedicated hosting environments.
What are common advantages of cloud hosting today and how does it streamline operations?
Cloud hosting today provides advantages of cloud such as elastic scalability, high availability, faster provisioning, and pay-as-you-go billing. These benefits help cloud hosting to streamline development and operations by enabling rapid deployment, automated scaling, and easier disaster recovery. Organizations using the cloud hosting model can shift from capital expenditure on servers to operational spending on cloud services, often improving agility and reducing time-to-market.
How secure is cloud hosting and what security features do cloud hosting providers offer?
Security in cloud hosting depends on the cloud hosting provider and the chosen hosting environment. Public cloud providers and cloud hosting companies typically offer encryption at rest and in transit, identity and access management, network firewalls, DDoS protection and compliance certifications. For added control, private cloud or hybrid cloud setups can isolate workloads. Customers must also follow best practices—secure configuration, patch management and application-level protections—because responsibility is shared between the provider and the user.
What are common hosting models and when should I select public cloud vs private cloud?
Common hosting models include shared hosting, VPS, dedicated servers, public cloud, private cloud and hybrid cloud. Choose public cloud when you need cost-effective scalability, broad geographic reach and easy integration with public cloud services from vendors like amazon web services or google cloud platform. Choose private cloud when you require strict data governance, predictable performance or compliance. A hybrid model is useful when you want to combine the control of private cloud with the elasticity of public cloud.
How do I migrate to a cloud hosting solution and what do cloud hosting companies recommend?
Migrating to a cloud hosting solution typically involves assessing your current hosting environment, identifying dependencies, selecting a cloud hosting provider, and planning a phased migration. Cloud hosting companies recommend starting with low-risk workloads, using replication and backup tools, testing in a cloud hosting environment, and optimizing resources to control costs. Leveraging cloud service features such as autoscaling, managed databases and object storage can improve performance and reliability once migration is complete.
What Should You Do Next After Learning About Cloud Hosting?
Now that you learn about cloud hosting, here’s what I’d suggest:
- Compare it with shared and vps hosting
- List your traffic and budget needs
- Check what hosting providers offer in the US
- Look for affordable hosting with clear pricing
- Decide if cloud fits your site right now
If not, start simple and grow later.
Final Thoughts
Let’s wrap this up in plain English.
Cloud hosting is about flexibility.
Your site runs on many systems, not just one. That means:
- Better uptime
- Easy scaling
- And steady performance
For US sites that are growing or expect traffic spikes, a cloud host can be a smart move.
But for brand-new beginners?
It might be more than you need today.
Bottom line?
Start where you are. Grow when you’re ready. And when flexibility matters, cloud hosting will be waiting for you.
