
Choosing between VPS vs Cloud Hosting can feel confusing, especially if you are trying to grow a website in 2026. Both hosting types promise better performance than shared hosting, but they work in very different ways.
This guide explains what VPS hosting and cloud hosting actually mean, how they differ, and which one makes more sense depending on your website goals. The goal is to help you avoid overpaying, underperforming, or choosing a hosting setup that limits growth.
What VPS and Cloud Hosting Mean
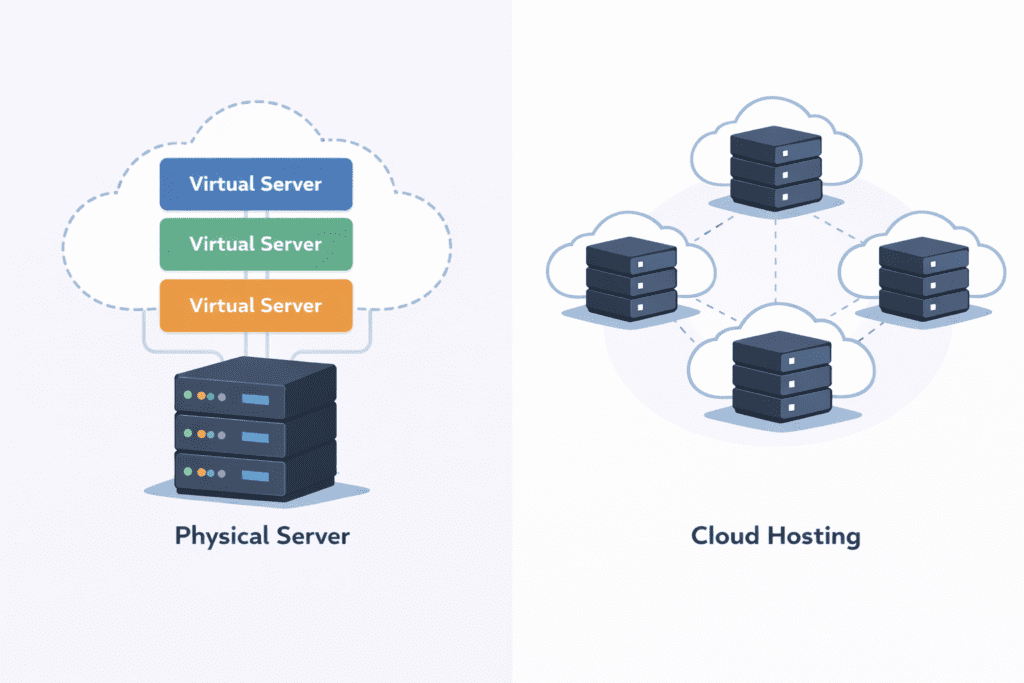
VPS hosting stands for Virtual Private Server hosting. It uses a single physical server that is divided into multiple virtual servers. Each VPS server has its own dedicated resources, even though it shares the same physical machine.
Cloud hosting works differently. Instead of relying on one server, cloud hosting uses multiple cloud servers connected together. Your website pulls resources from a cloud environment, not a single machine.
This core difference affects performance, reliability, pricing, and scalability.
Why Choosing the Right Hosting Type Matters
Your hosting choice affects website speed, uptime, security, and long-term costs. A poor hosting setup can slow down pages, cause downtime, or fail during traffic spikes.
In the VPS vs Cloud Hosting debate, the wrong decision often leads to:
- Paying for unused resources
- Running into scaling limits
- Unexpected billing issues
- Performance drops during growth
Choosing the right hosting solution early saves time and money later.
Who This Comparison Is For
This comparison is designed for:
- Bloggers who are outgrowing shared hosting
- Small businesses that need reliable performance
- Growing websites with traffic spikes
- Website owners planning long-term scalability
If shared hosting feels limiting, this guide will help you understand whether VPS hosting or cloud hosting fits your needs better.
What Is VPS Hosting?

VPS hosting stands for Virtual Private Server hosting. It is a type of web hosting where one physical server is divided into multiple virtual servers. Each virtual server works like an independent server with its own resources.
Unlike shared hosting, your website does not compete directly with other sites for basic server power. This is why many website owners move to VPS hosting when their site grows.
How VPS Hosting Works
VPS hosting uses virtualization technology. A powerful physical server is split into multiple virtual servers using software called a hypervisor. Each VPS server runs its own operating system and has its own server space.
Even though multiple VPS servers live on the same physical server, they act like separate machines. Your VPS hosting environment stays isolated from other users on the server.
This setup gives more control, stability, and flexibility compared to shared hosting.
Virtual Server Resources Explained
With VPS hosting, you get dedicated resources assigned to your virtual server. These resources usually include:
- CPU power
- RAM memory
- Storage space
- Bandwidth
Because these server resources are reserved for your VPS plan, performance stays more stable. Other websites on the same physical server cannot take your allocated resources.
This is one of the biggest advantages of VPS hosting compared to shared hosting plans.
Typical Use Cases for VPS Hosting
VPS hosting is commonly used by:
- Websites that outgrow shared hosting
- Blogs with steady traffic growth
- Small business websites
- Developers who need server control
- Sites running custom software
Many hosting providers recommend VPS hosting when shared hosting starts showing limits in speed or reliability.
Key Benefits of VPS Hosting
VPS hosting offers several important benefits:
- Better performance than shared hosting
- Dedicated resources for consistent speed
- More control over server settings
- Improved security due to isolation
- Ability to install custom software
For website owners who want more power without paying for dedicated hosting, VPS hosting is often a strong middle option.
Main Limitations of VPS Hosting
While VPS hosting is powerful, it does have limits:
- Costs more than shared hosting
- Requires some technical knowledge
- Scaling is usually manual
- Still relies on one physical server
If the physical server goes down, all VPS servers on it may be affected. This is where cloud hosting works differently, which we’ll cover next.
What Is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is a modern hosting solution that uses multiple connected servers instead of a single physical server. Your website runs inside a cloud environment, which means it can pull resources from more than one cloud server when needed.
In the VPS vs Cloud Hosting comparison, this difference plays a major role in performance, reliability, and scalability.
How Cloud Hosting Works
Cloud hosting works by spreading website data across a network of servers. Instead of relying on one machine, your site uses resources from a pool of cloud servers.
If one cloud server fails, another server steps in automatically. This makes cloud hosting more resilient than traditional VPS hosting.
Most cloud hosting providers use advanced load balancing to distribute traffic evenly across the cloud infrastructure.
Distributed Server Infrastructure
Unlike VPS hosting, cloud hosting does not depend on a single physical server. Your website exists inside a distributed system where multiple servers work together.
This distributed setup helps with:
- Reducing downtime risk
- Handling sudden traffic spikes
- Maintaining consistent website speed
Because of this structure, cloud hosting is often chosen by growing websites that cannot afford outages.
Typical Use Cases for Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is commonly used by:
- High-traffic websites
- E-commerce stores
- SaaS platforms
- Growing online businesses
- Websites with unpredictable traffic
When comparing VPS vs Cloud Hosting, cloud hosting usually fits websites that need flexibility more than fixed resources.
Key Benefits of Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting offers several advantages:
- High uptime due to multiple servers
- Easy scalability
- Pay-as-you-use pricing models
- Better performance during traffic spikes
- Strong redundancy and failover support
Many hosting companies promote cloud hosting as a long-term hosting solution for growing websites.
Main Limitations of Cloud Hosting
Despite its benefits, cloud hosting also has drawbacks:
- Pricing can be unpredictable
- More complex billing models
- Less control than unmanaged VPS hosting
- Can be confusing for beginners
Some website owners prefer VPS hosting because of its fixed pricing and simpler setup.
VPS vs Cloud Hosting – Quick Comparison
When people compare VPS vs Cloud Hosting, they usually want a clear answer to one question: Which one fits my website better right now?
This section breaks down the core differences in a simple, practical way.
Performance and Reliability
With VPS hosting, your website runs on a virtual private server created from a single physical server. You get dedicated resources, which helps performance stay stable-as long as that physical server stays healthy.
Cloud hosting works differently. Your site runs across multiple servers in a cloud environment. If one server has an issue, another cloud server takes over. That’s why cloud hosting is often seen as more reliable.
In short:
- VPS hosting = stable, predictable performance
- Cloud hosting = higher fault tolerance and uptime
Resource Allocation
VPS hosting gives you fixed resources like CPU, RAM, and storage. These resources are reserved only for your VPS server, which is great for consistency.
Cloud hosting uses flexible resource allocation. Your site can scale up or down based on demand, pulling power from the cloud when needed.
This is one of the biggest differences in VPS vs Cloud Hosting:
- VPS = fixed limits
- Cloud = flexible limits
Scalability
Scaling a VPS hosting plan usually means upgrading your VPS plan or moving to a larger virtual server. This process can involve downtime or manual changes.
Cloud hosting scales almost instantly. Resources can increase automatically during traffic spikes and scale back down afterward.
If growth is unpredictable, cloud hosting has a clear edge here.
Pricing Model
VPS hosting typically comes with fixed monthly pricing. You know what you’ll pay each month, which helps with budgeting.
Cloud hosting often uses a pay-as-you-go model. You pay based on usage, which can be efficient-but also harder to predict.
So in the VPS vs Cloud Hosting cost debate:
- VPS hosting = predictable bills
- Cloud hosting = flexible but variable costs
Ease of Management
VPS hosting often requires more technical knowledge, especially with unmanaged VPS plans. You’re responsible for server setup, updates, and security unless you choose managed VPS hosting.
Cloud hosting providers usually handle much of the infrastructure, making cloud platforms easier for non-technical users-especially with managed cloud hosting plans.
VPS vs Cloud Hosting: Performance & Reliability Comparison
When deciding between VPS vs Cloud Hosting, performance and reliability are usually the top concerns. Speed, uptime, and how well your site handles traffic spikes all affect real users in the US.
Speed and Load Times
With VPS hosting, your website runs on a virtual private server with dedicated resources. That means your site’s speed stays consistent because you’re not sharing CPU or RAM with random users.
Cloud hosting spreads your website across multiple servers. This setup often results in faster load times during busy periods because traffic is balanced across the cloud.
In day-to-day use, both options can be fast. The difference shows up when traffic changes suddenly.
Handling Traffic Spikes
This is where VPS vs Cloud Hosting becomes very clear.
VPS hosting has limits. If traffic goes beyond your VPS plan’s capacity, performance may drop unless you manually upgrade.
Cloud hosting handles spikes more smoothly. Extra resources are added automatically, then removed when traffic returns to normal.
“During a short promotion that brought roughly 5,000 visitors in one day, cloud hosting kept pages stable while a similar VPS setup needed a manual upgrade.”
That’s a practical example of how flexibility matters.
Uptime Consistency
VPS hosting depends on one physical server. If that server fails, your VPS can go offline until the issue is fixed.
Cloud hosting reduces this risk. If one cloud server fails, another takes over. This redundancy improves uptime and reliability.
For websites where downtime equals lost revenue, cloud hosting usually offers better protection.
Impact on User Experience
Speed and uptime directly affect user experience. Slow pages or outages can frustrate visitors and increase bounce rates.
With VPS hosting, performance is stable as long as traffic stays within limits. Cloud hosting adapts better to changing conditions, which helps maintain a smoother experience.
From a user’s point of view, the better option is the one that stays fast and available when it matters most.
Scalability & Flexibility
Scalability is one of the biggest decision points in the VPS vs Cloud Hosting debate. This section focuses on how each option grows with your website and how much flexibility you really get.
Scaling with VPS Hosting
With VPS hosting, scalability is structured but limited. Your VPS plan comes with fixed server resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage. When your site grows beyond those limits, you usually need to upgrade to a larger VPS plan.
That upgrade often means:
- Choosing a new VPS plan
- Migrating data or restarting services
- Possible downtime during the change
VPS hosting works well when growth is predictable. If traffic increases slowly and steadily, upgrading a VPS plan is manageable.
Scaling with Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is built for flexibility. Instead of upgrading a single virtual server, cloud hosting pulls resources from multiple servers in real time.
When traffic increases:
- Resources scale automatically
- No manual intervention is needed
- Performance stays consistent
This is a key advantage in VPS vs Cloud Hosting, especially for websites with seasonal traffic or sudden spikes.
Vertical vs Horizontal Scaling
VPS hosting mainly uses vertical scaling. That means adding more power to one virtual server.
Cloud hosting uses horizontal scaling. It adds more servers instead of pushing one server harder.
Vertical scaling has limits. Horizontal scaling is more flexible and reduces risk during high traffic periods.
Best Choice for Growing Websites
If your website has predictable growth and stable traffic patterns, VPS hosting can be a reliable and cost-controlled option.
If growth is uncertain, traffic varies, or uptime is critical, cloud hosting is usually the better long-term choice.
This is why many hosting providers recommend cloud hosting for fast-growing or business-critical websites.
VPS vs Cloud Hosting: Pricing & Cost Structure
Pricing often decides the final choice in the VPS vs Cloud Hosting comparison. While both options can support growing websites, they handle costs very differently.
VPS Hosting Pricing Model
VPS hosting usually comes with fixed monthly pricing. You choose a VPS plan based on server resources like CPU, RAM, and storage, and the price stays the same every month.
This structure makes budgeting easier. Website owners know exactly what they’ll pay, even during traffic spikes.
However, if your site outgrows the VPS plan, you’ll need to upgrade to a higher-tier VPS hosting plan, which increases the monthly cost.
Cloud Hosting Pay-As-You-Go Pricing
Cloud hosting uses a usage-based pricing model. Instead of fixed limits, you pay for the resources your site actually uses.
This can be cost-effective for sites with uneven traffic, but it also means:
- Monthly bills may change
- Costs can rise quickly during traffic surges
- Budgeting requires closer monitoring
In VPS vs Cloud Hosting, this pricing difference often surprises beginners.
Cost Predictability
VPS hosting offers predictable costs. You pay the same amount regardless of traffic changes, as long as you stay within resource limits.
Cloud hosting is less predictable. While you only pay for what you use, heavy traffic or misconfigured resources can increase costs without warning.
This is an important factor for small businesses and bloggers working with fixed budgets.
Long-Term Cost Comparison
Over the long term:
- VPS hosting is often cheaper for stable websites
- Cloud hosting can cost more as traffic and usage grow
Cloud hosting becomes more cost-effective only when its flexibility prevents downtime, lost sales, or performance issues that would otherwise hurt revenue.
Choosing between VPS vs Cloud Hosting isn’t about which is cheaper-it’s about which cost model fits your website’s behavior.
How to Choose Between VPS and Cloud Hosting
If you’re still deciding between VPS vs Cloud Hosting, this section brings everything together in a practical way. There’s no universal winner. The right choice depends on how your website behaves today and where it’s headed next.
Website Size and Traffic Expectations
If your website has steady traffic and predictable growth, VPS hosting is often enough. A VPS server gives you dedicated resources and stable performance without surprises.
If traffic changes often, or you expect sudden growth, cloud hosting adapts better. Cloud platforms handle spikes automatically, which reduces risk during busy periods.
Budget and Billing Preference
VPS hosting works well if you want consistent monthly bills. You pay for a fixed VPS plan and don’t have to track usage closely.
Cloud hosting fits users who are comfortable with variable costs. You pay based on usage, which can be efficient-but only if monitored.
When comparing VPS vs Cloud Hosting, budgeting style matters just as much as performance.
Performance and Uptime Needs
For websites where uptime is critical, cloud hosting offers stronger protection. Multiple servers mean fewer single points of failure.
VPS hosting is reliable too, but it still depends on one physical server. If that server goes down, your site may be affected.
Technical Experience Level
VPS hosting often requires more technical knowledge, especially unmanaged VPS setups. You may need to handle server updates, security, and configuration.
Cloud hosting-especially managed cloud hosting-is usually easier for non-technical users. Many hosting providers handle infrastructure tasks for you.
Future Growth Plans
If you expect slow, steady growth, VPS hosting can scale step by step.
If growth is uncertain or fast, cloud hosting gives you room to expand without planning every upgrade in advance.
FAQs – VPS vs Cloud Hosting
Is cloud hosting better than VPS?
Cloud hosting isn’t always better. It’s more flexible, but VPS hosting can be more affordable and predictable for stable websites.
Which is more scalable, VPS or cloud hosting?
Cloud hosting is more scalable. Resources adjust automatically, while VPS hosting requires manual upgrades.
Is VPS hosting cheaper than cloud hosting?
In many cases, yes. VPS hosting often costs less over time for sites with consistent traffic.
Do I need technical skills for cloud hosting?
Not always. Managed cloud hosting reduces technical work, while unmanaged cloud setups require more experience.
Can I switch from VPS to cloud hosting later?
Yes. Many hosting providers allow upgrades or migrations from VPS hosting to cloud hosting as your needs change.
What is the main difference between VPS and cloud hosting?
The core difference between VPS and cloud is architecture: a traditional VPS partitions a single physical server into multiple virtual private servers, while cloud hosting runs across a pool of servers managed by cloud providers. A VPS solution gives fixed resource allocations on one server, whereas cloud hosting services scale resources across many machines, offering higher redundancy and flexibility for changing hosting needs.
How do pros and cons compare for cloud and VPS hosting?
Pros and cons depend on use case: pros of cloud include scalability, high availability, and easy growth; cons may include variable costs and complexity. VPS pros include predictable pricing, dedicated-like resources, and simpler management; cons include limited scalability and single-server failure risk. Consider pros and cons of VPS and cloud and whether you need a hosting service that prioritizes elasticity or fixed resource control.
When should I choose cloud or VPS hosting for a web project?
Choose cloud hosting when you expect variable traffic, need fast scaling, or require fault tolerance across cloud providers or private cloud instances. Use VPS when you want a cost-effective, stable environment with predictable performance and root access – for example, small web hosting, staging servers, or projects where budget matters more than instant scaling.
Is VPS hosting vs cloud hosting better for e-commerce and high-traffic sites?
For high-traffic e-commerce sites, cloud hosting is often better because the cloud hosting platform can handle spikes and distribute load across nodes; cloud and VPS hosting compare by offering different resilience levels. A VPS might be adequate for small-to-midsize stores, but growth-focused or mission-critical stores usually prefer cloud and cloud providers that offer autoscaling and redundancy.
Can I migrate from VPS to cloud hosting services easily?
Yes, migration from a traditional VPS to cloud hosting services is common: many hosting providers offer migration tools or managed services to move your server from a single server to a cloud environment. Plan for differences in networking, storage, and backup strategies – see how cloud architectures differ and test the application in the cloud before switching production traffic.
How do costs compare between cloud hosting vs VPS hosting?
Costs vary: VPS hosting typically has fixed monthly prices and predictable vps offers, while cloud hosting often uses consumption-based pricing that can be cost-efficient for variable loads but may be higher under constant heavy use. Compare provider offers, expected usage patterns, and whether the hosting service includes managed support, backups, and monitoring.
Do I get better security with cloud hosting and VPS hosting compare?
Security depends on configuration and provider: cloud providers and VPS hosts both provide security controls, but cloud hosting services can offer advanced network isolation, private cloud options, and automated security tools. A VPS gives you more direct control over hardening the server, while cloud environments give built-in features for encryption, identity, and monitoring when configured correctly.
What about performance – does a VPS give better speed than cloud?
Performance depends on resource allocation and workload: a well-provisioned VPS can give consistent, low-latency performance since resources are dedicated on one physical server. Cloud hosting can match or exceed that performance through optimized cloud hosting solutions and autoscaling, but noisy neighbors or multi-tenant setups can affect some cloud vps-style instances unless you choose dedicated or reserved instances.
Are there hybrid options combining shared hosting, dedicated hosting, and cloud or VPS?
Yes, many hosting providers offer hybrid hosting solutions that mix shared and dedicated hosting with cloud and VPS options. You can run front-end services on a cloud hosting platform, keep databases on a dedicated server hosting instance for consistent I/O, and use VPS servers for development or staging – choose a hosting service that fits your architecture and long-term hosting industry trends.
How do I decide between cloud vps, private cloud, or traditional VPS for my team?
Decide based on scale, control, and compliance: choose traditional VPS for small teams wanting straightforward control and lower cost; choose cloud vps or private cloud if you need scalability, multi-region deployments, or specific compliance controls. Evaluate hosting providers offer, managed services, and whether the provider’s cloud hosting platform supports your software stack and anticipated growth.
Final Verdict – VPS vs Cloud Hosting: Which One Is Right for You?

The choice between VPS vs Cloud Hosting comes down to control versus flexibility.
VPS hosting is a strong option if you want predictable costs, dedicated resources, and steady performance. It works well for websites with stable traffic and clear growth patterns.
Cloud hosting is better if flexibility matters more than fixed pricing. It handles traffic spikes, improves uptime, and scales easily-but requires closer cost monitoring.
Bottom line?
Choose VPS hosting for stability and budget control.
Choose cloud hosting for scalability and resilience.
Both are solid hosting options. The right one depends on how your website grows and how much flexibility you want moving forward.
