If you run a website in the US, security is no longer optional. One of the most important security tools today is SSL. Many beginners ask, what is SSL, and why almost every modern website uses it.
This guide explains what is SSL, how it works, and why it matters for US websites. You’ll learn how an SSL certificate protects visitors, builds trust, and supports SEO. By the end, you’ll clearly understand why your site needs SSL and how it keeps data safe across the internet.
For US businesses, blogs, and online stores, SSL is now a basic requirement. Browsers warn users when a site is not secure, and that can scare visitors away. That’s why SSL plays a key role in website security, user trust, and search visibility.
What Is SSL? (Simple Definition)
So, what is SSL in simple words?
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It is a security technology that creates a secure connection between a browser and a server. This secure connection keeps information private while it travels across the web.
An SSL certificate is a digital file installed on a web server. It tells the browser that the website is trusted and safe to visit. When a site uses SSL, the address starts with HTTPS instead of HTTP.
Even though SSL has been replaced by Transport Layer Security, the term SSL is still commonly used to describe website security certificates. You’ll often see SSL and TLS mentioned together as SSL and TLS.
Without an SSL certificate, data sent between a website and a visitor can be intercepted. That’s why websites that collect passwords, emails, or credit card details must use SSL.
What Does SSL Do for a Website?
An SSL certificate performs three main jobs.
1. Encrypts Data
SSL uses encryption to scramble data before it moves across the internet. This means hackers cannot read or intercept the information. SSL encrypts sensitive data like login details and payment information.
This ssl encryption ensures that private information stays protected between the browser and the web server.
2. Protects User Information
When users enter personal or sensitive information, SSL keeps it safe. It prevents attackers from trying to intercept data during transmission.
This protection is essential for any website that asks users to sign up, log in, or submit forms.
3. Builds Trust With Visitors
Browsers show security indicators when a website has a valid ssl certificate. Visitors see the padlock icon and feel safer browsing the site.
A site that has an SSL looks professional and trustworthy. That trust helps improve user confidence, engagement, and conversions.
How SSL Works (Step by Step)
To understand how SSL works, let’s break it down simply.
When a user visits a website, the browser and the web server begin an SSL handshake. During this process:
- The browser requests a secure connection
- The server sends its ssl certificate
- The browser verifies the certificate with a certificate authority
- A secure SSL connection is created using a public key and private key
Once the SSL handshake is complete, all data shared between the browser and the server is encrypted. This secure connection protects information as it travels across the web.

You’ve probably noticed that some websites start with HTTP, while others use HTTPS. That extra “S” is important.
HTTPS means Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It shows that a website is protected by an SSL certificate. When a site uses SSL, the browser and server communicate over an encrypted connection.
Without SSL, a site stays on HTTP. That means data moves in plain text. Anyone with the right tools could try to intercept that data. This is why modern browsers warn users before loading sites without an SSL certificate.
In short:
- HTTP = not secure
- HTTPS = secured using SSL or TLS
Google and other search engines prefer HTTPS websites. Browsers also mark HTTPS sites as secure, which improves trust with US visitors.
Types of SSL Certificates
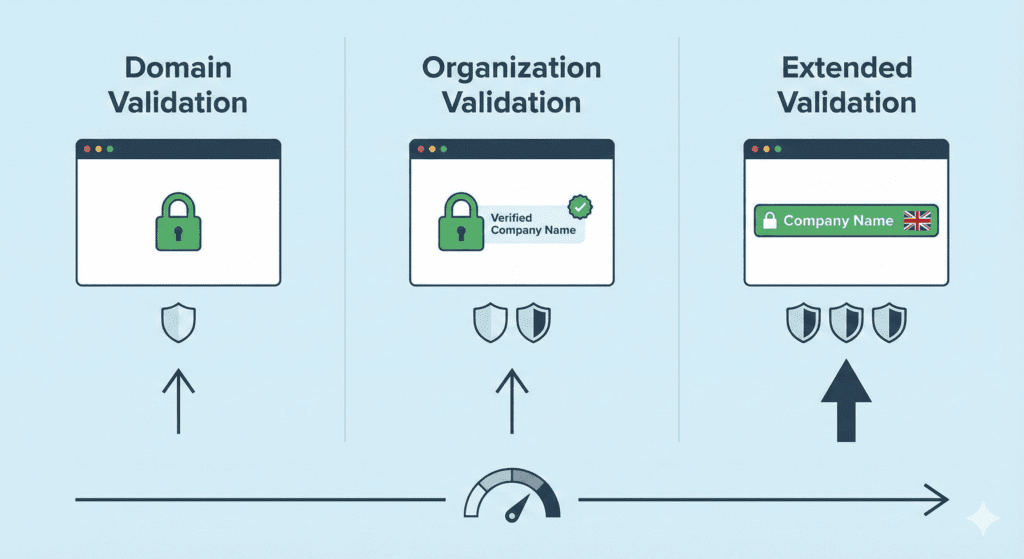
There are different certificate types, and choosing the right one depends on your website’s purpose.
Domain Validation (DV)
A DV certificate is the most basic type of SSL certificate. It only checks if you control the domain name.
- Fast to issue
- Often comes as a free SSL certificate
- Common for blogs and small websites
Most beginners start with DV SSL because it’s easy and affordable.
Organization Validation (OV)
OV certificates verify both the domain and the organization behind it.
- Shows business information
- More trust than DV
- Good for business websites
This type of SSL offers a higher level of security you need for professional sites.
Extended Validation (EV)
Extended Validation certificates offer the highest trust level.
- Strong identity checks
- Best for large brands and financial sites
- Often used for handling credit card payments
EV SSL certificates help users feel confident that a site is legitimate.
Other SSL Options
Some sites need more flexibility:
- Wildcard SSL certificate protects a domain and all its subdomains
- Multi-domain SSL certificates secure multiple domains with one certificate
These options are helpful for growing websites and businesses.
Why SSL Is Important for US Websites

For US website owners, SSL is not just about security. It affects trust, SEO, and compliance.
Builds User Trust
When a browser shows a security warning, most users leave. A website with SSL looks safer and more professional.
This trust matters for online forms, logins, and checkout pages.
Helps With SEO
SSL is a known ranking signal. Google has confirmed that HTTPS is a positive factor for SEO.
While SSL alone won’t rank a site, it supports better visibility in search results.
Meets Privacy Expectations
US users expect websites to protect their data. SSL helps meet basic privacy and security standards.
Many regulations and platforms now require SSL to operate safely online.
Does SSL Affect Website Performance?
Some beginners worry that SSL slows down a website. That used to be true years ago, but not anymore.
Modern ssl encryption is fast and efficient. Most browsers and servers are optimized for HTTPS.
In most cases:
- SSL has little to no impact on speed
- Some sites even load faster with HTTPS
So, SSL improves security without hurting performance.
Free vs Paid SSL Certificates

Many beginners ask the same question: Do I need to buy SSL, or is free SSL enough?
The answer depends on what kind of website you run.
What Free SSL Offers
A free SSL certificate usually comes from providers like Let’s Encrypt and is often included with your web hosting plan.
Free SSL:
- Encrypts data using strong ssl encryption
- Secures your domain with HTTPS
- Works well for blogs, personal sites, and small businesses
- Renews automatically in most cases
For most beginners, free SSL is more than enough to secure your website and meet basic SEO and trust needs.
When Paid SSL Makes Sense
A paid SSL certificate may be useful if:
- You run an online store
- You collect sensitive information
- You want higher business trust indicators
Paid SSL options often include:
- Organization or extended validation
- Warranty and support
- Brand trust signals
That said, paid SSL does not magically improve rankings or speed. It mainly adds identity verification.
For many US websites, free SSL is the smart starting point.
How to Get an SSL Certificate
Getting an SSL certificate today is much easier than it used to be.
Through Your Hosting Provider
Most hosting providers include SSL by default.
Many web hosting services:
- Offer one-click SSL setup
- Provide free SSL certificates
- Handle renewals automatically
This is the easiest option for beginners.
From a Certificate Authority
You can also obtain an SSL certificate directly from a certificate authority.
The process usually involves:
- Generating a certificate signing request
- Proving you control the domain
- Installing the certificate manually
This method is more technical and usually unnecessary for beginners.
How to Install and Enable SSL on a Website
The exact steps depend on your host, but the process is usually simple.
General Installation Steps
- Log in to your hosting provider dashboard
- Find the SSL or security section
- Enable SSL for your domain name
- Wait for the certificate to be issued
- Force HTTPS on your website
Most hosts handle the ssl handshake automatically between the browser and the server.
For WordPress Websites
If you use WordPress:
- Many hosts auto-install SSL
- You may need to update site URLs to HTTPS
- A plugin can help redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Once installed, your website has an SSL certificate and loads securely.
Common SSL Mistakes Beginners Make
Even with simple setup, mistakes happen.
Mixed Content Issues
This happens when:
- Your site loads over HTTPS
- Some images or scripts still load over HTTP
Browsers may still show warnings. Updating all links fixes this.
Expired Certificates
If SSL doesn’t auto-renew, your site may break.
Always:
- Enable automatic renewal
- Monitor certificate status
Not Redirecting HTTP to HTTPS
If visitors can still access HTTP:
- Data may not be encrypted
- SEO signals may split
A proper redirect ensures all traffic uses HTTPS.
Does SSL Protect Against Hacking?
This is an important clarification.
SSL:
- Encrypts data
- Protects data in transit
- Prevents interception
But SSL doesn’t:
- Stop malware
- Prevent hacked passwords
- Replace full website security
SSL is one layer of security, not total protection.
FAQs – SSL and Website Security
Let’s clear up a few common questions beginners in the US usually have.
Is SSL Required for All Websites?
Technically, a website can exist without SSL. But in reality, you need SSL.
Without an SSL certificate:
- Browsers mark your site as “Not Secure”
- Visitors lose trust fast
- Some features may not work correctly
Even simple blogs should use SSL today. Running a site without an SSL certificate sends the wrong signal to users and search engines.
Does SSL Protect Against Hacking?
This is where many people get confused.
SSL:
- Encrypts data between the browser and the web server
- Protects login details and forms
- Prevents data from being intercepted
But SSL isn’t a full security system.
It doesn’t:
- Remove malware
- Stop brute-force attacks
- Replace backups or firewalls
SSL certificates protect data in transit. You still need basic website security practices.
How Often Does SSL Need Renewal?
It depends on the certificate.
- Free SSL certificates usually renew every 90 days automatically
- Paid SSL may renew yearly or every two years
Most modern hosting setups handle renewals for you. Still, it’s smart to check once in a while to avoid surprises.
Can SSL Break a Website?
Sometimes, yes – but it’s fixable.
Issues usually come from:
- Mixed content (HTTP files on HTTPS pages)
- Incorrect redirects
- Hard-coded links
These problems are common and easy to fix. SSL itself doesn’t break sites – configuration mistakes do.
What Should You Do Next After Setting Up SSL?
Once SSL is active, don’t stop there.
Test HTTPS Properly
Open your site in a browser and:
- Check for the padlock icon
- Confirm HTTPS loads on every page
- Test both www and non-www versions
Your website with SSL should redirect all traffic securely.
Update Internal Links
Make sure:
- Images load over HTTPS
- Scripts and stylesheets use HTTPS
- Internal links point to HTTPS URLs
This prevents warnings and improves trust.
Monitor Certificate Status
Even if SSL auto-renews:
- Set reminders
- Check your hosting dashboard
- Watch for browser warnings
A valid SSL certificate is something you don’t want to lose.
Why SSL Still Matters in 2026
Some people ask if SSL is still relevant.
Short answer: yes, more than ever.
SSL:
- Protects users across the internet
- Supports SEO signals
- Builds trust instantly
- Helps meet privacy expectations
Search engines expect secure websites. Users expect security too. Running a site without SSL certificates puts you behind from day one.
Final Thoughts
So, what is SSL, really?
SSL is the basic foundation of website trust.
It:
- Encrypts data
- Protects visitors
- Makes your site look professional
- Supports SEO and user confidence
The good news? You don’t need advanced skills or expensive tools. Most US website owners can secure their site in minutes using their web hosting provider.
Bottom line:
If you care about your visitors, your reputation, and your future growth, SSL isn’t optional anymore. It’s just part of running a modern website.
