
Here’s what I noticed when beginners in the US start comparing hosting options: sooner or later, someone brings up VPS hosting. It usually happens right after they outgrow shared hosting or hear their web host say, “You might need more power.”
From my research, VPS comes up when:
- A site feels slow on shared plans
- Traffic starts growing
- People want more control over the server
- Or they see errors and limits they can’t fix
This guide will help you:
- Understand what a virtual private server really is
- Learn how vps hosting works on a real physical server
- See how it compares with shared, dedicated hosting, and cloud hosting
- And decide if you should use vps for your site in the US
Let’s keep it simple. No heavy tech talk. Just clear answers.
What Is VPS Hosting? (Simple Definition)
In plain English, VPS hosting means your website runs on a private virtual space inside a bigger server.
A virtual private server is created when one big physical server is divided into smaller parts. Each part acts like its own virtual server with its own system, space, and settings.
So the simple idea is:
VPS hosting gives you a private slice of a server that feels like your own server.
Even though you still share the main machine, your VPS acts like an independent server.
That’s why many people say VPS is the middle ground between shared hosting and a dedicated server.
You’ll also hear VPS described as a virtual machine running inside a virtual environment on a real server.
How VPS Hosting Works
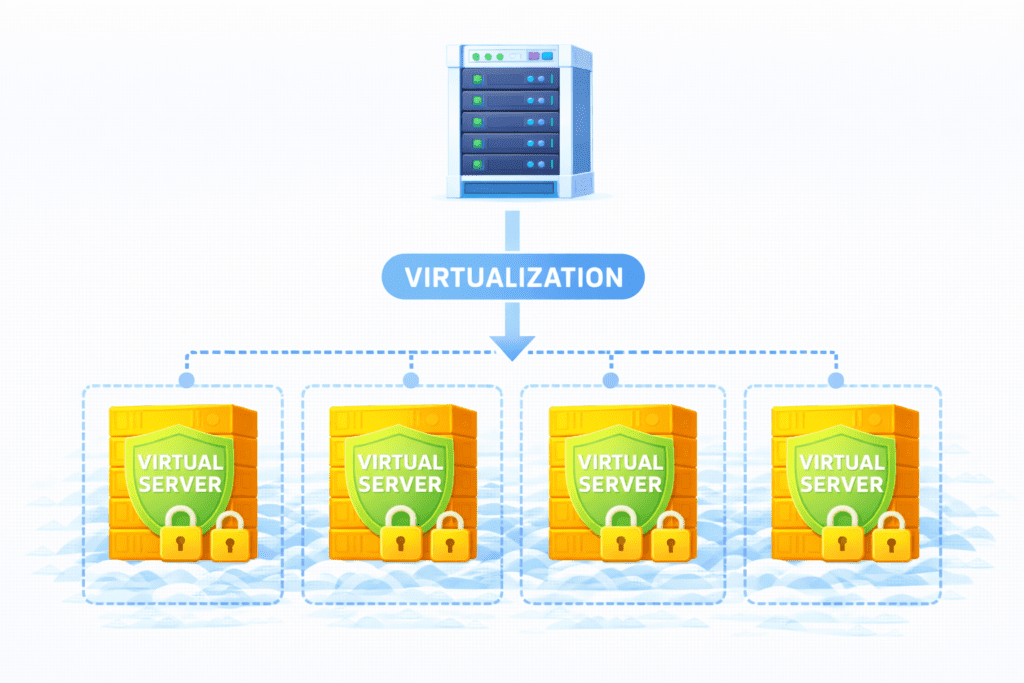
This is where things start to click.
One Physical Server, Multiple Virtual Servers
With VPS:
- There is one big physical server
- That server is split into multiple virtual parts
- Each part becomes a vps server
So many VPS users share the same physical server, but each one gets their own space.
You might also hear it explained as:
The server is divided into several virtual systems.
Each one acts like a standalone server for its user.
How Resources Are Isolated
Each VPS gets:
- Its own RAM
- Its own CPU share
- Its own storage
These are your server resources. Other users can’t touch them.
This setup creates an isolated virtual environment.
That’s why VPS feels much more private than a shared hosting environment.
Even though the physical server is still shared, your VPS runs in a protected space.
This is the heart of vps technology.
What Makes VPS Hosting Different From Other Hosting Types
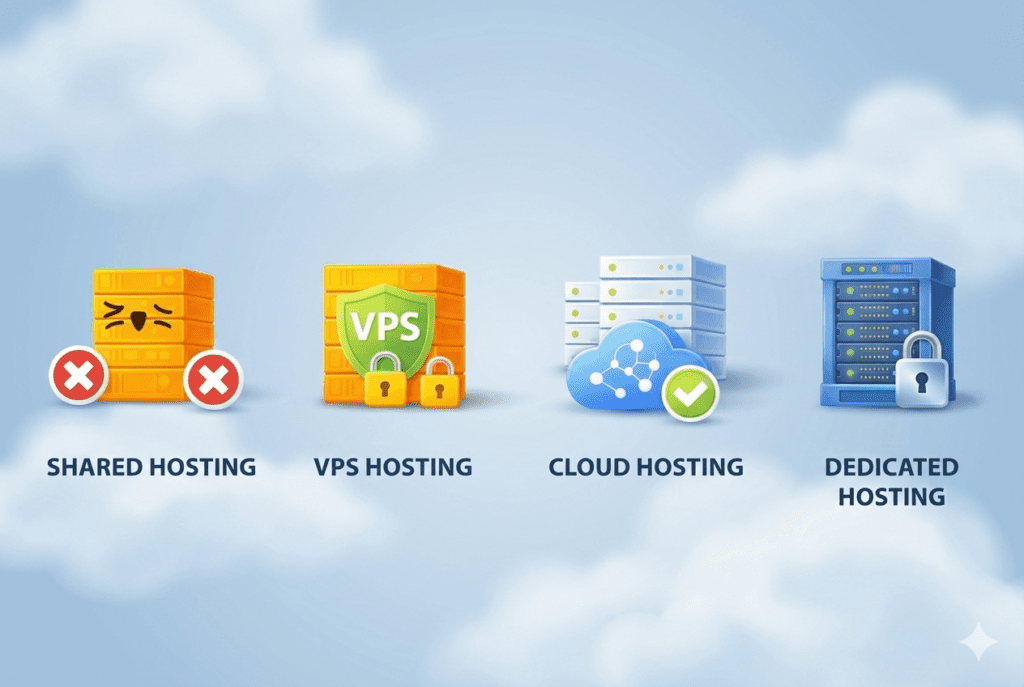
Let’s compare VPS with the options beginners usually know.
VPS vs Shared Hosting
With shared hosting:
- Many sites run on one server
- All users fight for the same power
- One bad site can slow others
With VPS:
- You get your own virtual server
- Your resources are reserved
- More stable performance
That’s why people say VPS is better compared to shared hosting.
In simple terms:
Shared = roommates.
VPS = your own apartment in the same building.
Also, shared hosting may be fine for tiny sites, but it has limits.
VPS vs Dedicated Hosting
With dedicated hosting, you rent an entire physical server just for you. That’s powerful but expensive.
With VPS:
- You don’t get the whole machine
- But you get a private space
- At a much lower cost
This is why people compare vps and dedicated hosting. VPS gives many benefits of a dedicated server without the full price.
VPS vs Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting spreads your site across many systems. VPS usually lives on one main machine.
Cloud is about flexibility across many servers.
VPS is about control on one server.
Some VPS plans are built on cloud systems, but classic VPS stays tied to one single physical server.
So when people debate vps and shared hosting or VPS vs cloud, it’s about control vs flexibility.
What Do You Get With VPS Hosting?
So what does vps hosting provides in real life?
Dedicated Resources
Your VPS comes with reserved RAM and CPU. No sharing like shared plans. That’s why vps provides better stability.
More Control
You get more control over server settings:
- Install software
- Change configs
- Run custom tools
You often get access to the server that shared users don’t.
Better Performance Than Shared Hosting
Because resources are isolated, VPS runs faster and more consistently than shared hosting.
That’s the big selling point for most people.
Many vps hosting services highlight this as their main advantage.
Who Should Use VPS Hosting in the US?
VPS isn’t for everyone, but it fits well for:
Growing Websites
If your site is growing and shared plans feel tight, a vps server can handle more traffic.
Medium-Traffic Blogs
Blogs with steady readers that need speed often move to VPS.
Small to Mid-Size Businesses
For US businesses that need reliability without the cost of a dedicated server, VPS is a smart hosting solution.
From what I’ve seen, most people move to VPS when shared hosting starts to feel like a bottleneck.
Who Should NOT Use VPS Hosting?
Even though VPS hosting is powerful, it’s not always the right move.
From my research, you probably should not jump into a vps server if:
Brand-New Beginners
If you’re a total beginner who just launched a site, shared hosting is usually enough. VPS adds choices and settings that can feel overwhelming.
Very Small Sites
If your site gets very little traffic, a full VPS hosting plan might be more than you need.
Users Who Don’t Want Technical Tasks
With VPS, you may need to:
- Handle updates
- Tweak server configuration
- Think about server management
If that sounds stressful, shared hosting or managed options are easier.
In most cases, people outgrow shared hosting first, then move to VPS.
Key Benefits of VPS Hosting

Let’s talk about why so many US users choose vps hosting.
Improved Performance
Because your VPS has its own server resources, your site won’t slow down when neighbors get busy. That’s a big step up from a shared hosting environment.
Better Stability
Your site runs in an isolated virtual environment, so problems on another account won’t crash your site.
Greater Customization
You get more freedom:
- Install tools
- Adjust server settings
- Choose your stack
That’s real control over server behavior.
More Security Than Shared Hosting
With isolation, your data stays safer than on shared plans. Many providers also add extra security features.
This advantage of vps is why growing sites move up.
Downsides of VPS Hosting

Let’s be real for a second. VPS isn’t perfect.
Higher Cost Than Shared Hosting
A VPS costs more than shared hosting. It’s still cheaper than dedicated hosting, but it’s not the lowest option.
Technical Management Needs
Unless you choose managed vps hosting, you’ll need some comfort with:
- Updates
- Fixing errors
- Basic server maintenance
Learning Curve
Even if you don’t touch everything, VPS comes with more choices. That can feel heavy at first.
Honestly, this is where many beginners hesitate — and that’s normal.
How Much Does VPS Hosting Cost in the US?
Prices vary by hosting provider, but here’s a simple range:
- Entry VPS: $10–$25/month
- Mid-range VPS: $30–$60/month
- High-end VPS: $80+/month
Cost depends on:
- RAM & CPU
- Storage
- Bandwidth
- Whether it’s managed vps or unmanaged vps
A good hosting plan should match your traffic and apps. Don’t overbuy early.
From what I’ve seen, many start around $20–$30 and upgrade as needed.
Is VPS Hosting Secure?
Short answer: yes, usually.
Because VPS runs in an isolated virtual space:
- Other users can’t touch your files
- You avoid most shared risks
Most vps hosting provider setups include:
- Firewalls
- Monitoring
- Regular patches
But here’s the thing…
If you manage it yourself, you’re responsible too. That means:
- Strong passwords
- Updates
- Watching logs
This is why many people choose managed and unmanaged hosting carefully.
VPS Security in Practice
With good setup:
- vps security is strong
- You’re safer than shared hosting
- Still cheaper than full dedicated server security stacks
Do You Need Technical Skills for VPS Hosting?
This depends on the type of VPS you choose.
Managed VPS Hosting
With managed vps hosting:
- The provider handles server maintenance
- They update software
- They fix common issues
This is great if you want power without stress.
Unmanaged VPS Hosting
With unmanaged vps hosting:
- You manage the server
- You handle updates
- You fix errors
This is for users who are comfortable with Linux and setups.
There’s also semi-managed vps hosting, which sits in between.
If you don’t want to deal with tech, go managed. Simple.
VPS Hosting vs Other Hosting Options (Quick Summary)
Here’s the simple breakdown:
- Shared hosting: cheapest, easiest, least power
- VPS hosting: balanced power, control, fair price
- Dedicated hosting: max power, full cost
- Cloud hosting: flexible scaling across systems
VPS is often the option compared to shared hosting when people want more speed but not full dedicated costs.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make With VPS Hosting
Most people mess up in a few common ways:
Upgrading Too Early
They move from shared hosting to VPS before they really need it.
Underestimating Management
They pick unmanaged VPS and realize they can’t deal with server tasks.
Choosing Wrong Specs
Too little RAM causes internal server errors.
Too much RAM wastes money.
Ignoring the Provider
Not all vps providers offer good support. Always check reviews.
Is VPS Hosting Good for Beginners?
Bottom line?
For most beginners: No, not at first.
But for beginners who:
- Already used shared hosting
- Want more control
- Are willing to learn
Then yes, VPS can make sense.
Often, people move from shared hosting to a vps when traffic grows.
FAQs About VPS Hosting
Let’s answer the most common questions beginners in the US ask about VPS hosting.
What is VPS hosting used for?
VPS hosting is used for websites and web applications that need more speed, control, and stability than shared hosting can offer. Many people use a vps server for growing blogs, business sites, or even an email server.
Is VPS better than shared hosting?
In most cases, yes. Vps hosting gives you dedicated resources and isolation, while shared hosting may slow down when neighbors use too much power. That’s why many upgrade when traffic grows.
Can I upgrade later?
Yes. Most hosting provider options let you scale your VPS or even move to dedicated hosting later. You won’t be stuck with one size forever.
How long does setup take?
Usually minutes to a few hours. Some providers auto-deploy your virtual private server. More complex setups may take longer, especially if you customize server configuration.
What Should You Do Next After Learning About VPS Hosting?
Now that you understand this beginner’s guide to virtual private servers, here’s what I’d suggest:
Compare Hosting Types
Look again at:
- shared hosting
- cloud hosting
- VPS vs dedicated server
Make sure VPS really fits your hosting needs.
Choose a VPS Carefully
When you’re ready, choose a vps based on:
- RAM & CPU
- Storage
- Support quality
- Whether it’s managed or unmanaged
A good vps hosting provider will clearly explain what their provider offers.
Start Small
Pick a modest hosting plan and grow later. You can always add resources as traffic rises.
Prepare to Manage
Even with managed plans, learn basic server management so you’re not lost if something breaks.
Final Thoughts
So, what’s the simple takeaway?
VPS hosting gives you a private, powerful space on a server without paying for an entire physical server. It sits right between shared hosting and dedicated hosting — more control than shared, less cost than dedicated.
If your site is growing and shared hosting feels tight, a virtual private server could be the right move. It runs in an isolated virtual environment on a single physical server, giving you better performance and stability.
But let’s keep it real:
If you’re just starting, shared hosting is often enough.
Move to VPS when you actually need it.
Bottom line?
Use VPS when your site outgrows shared hosting — not before.
Once you get this part, choosing the right hosting path feels much easier.
